给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例 1:
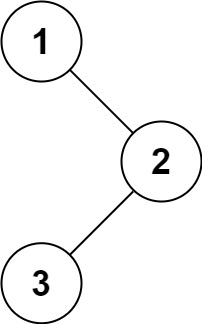
1
2
| 输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
|
示例 2:
示例 3:
示例 4:
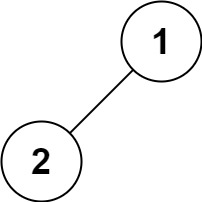
1
2
| 输入:root = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
|
示例 5:
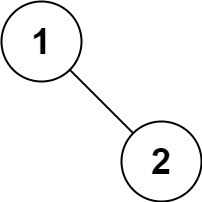
1
2
| 输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:[1,2]
|
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
中序递归
递归方法很简单,在这里不再赘述其原理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversalRec(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root, ans);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, List<Integer> ans) {
if (root == null) return;
dfs(root.left, ans);
ans.add(root.val);
dfs(root.right, ans);
}
}
|
复杂度分析:
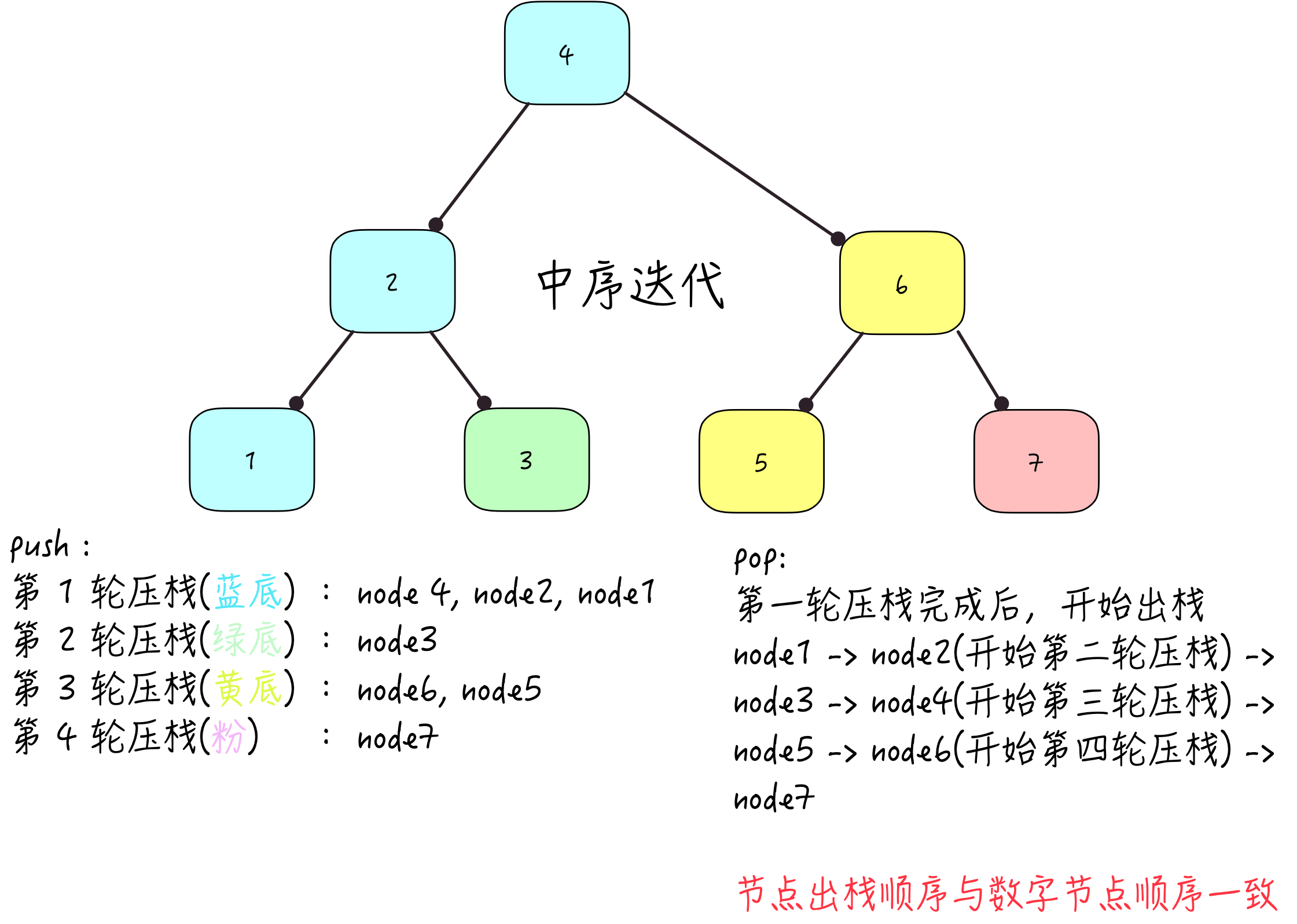
中序迭代
此方法与递归在时间,空间上来说没多大优势,但解决了递归深度如果过高时会栈溢出的风险。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class Solution2 {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.offerLast(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pollLast();
assert root != null;
ans.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return ans;
}
}
|
复杂度分析:
空间复杂度: O(N)
时间复杂度: O(N)
中序 Morris
Morris 遍历跟上述两种方法不同点在于,不需要递归或者临时的栈空间来辅助完成中序遍历,空间复杂度: 常数级别, O(1)。
但是为了解决从 child 树 到 parent 树,需要临时修改树的结构,也就是说会失去树本身带来的数据结构优势,仅仅是为了完成遍历,所带来的缺陷,但不要着急,用完以后将指针还原即可
为了更好的理解原理笔者代码整个遍历的过程中值需要当前 cur 和 临时 predecessor 2个指针, 具体步骤如下:
如果左子树节点为空, 将当前节点 val 添加到结果集 res 中,cur 指向其右子树 right 节点 (cur = cur.right)
如果左子树不为空, 遍历左子树的最右侧 right 子节点 (predecessor),在寻找的过程中会出现以下 2 种之一场景:
- predecessor.right 为空时,将 right 指针指向 cur 节点, cur 指向其左子树节点 (cur = cur.leftcur=cur.left)
- predecessor.right 不为空时, 表示原来的叶子节点连接已经存在(已经遍历完 cur.left)
- 将 predecessor.right = null
- cur 节点 val 添加到结果集 res 中 res.add(cur.val)
- cur 指向 其 right 节点 (cur = cur.right)
重复以上 2 步直到 cur 节点为空
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.left == null) {
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
} else {
TreeNode predecessor = cur.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != cur) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
if (predecessor.right == null) {
predecessor.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
} else {
res.add(cur.val);
predecessor.right = null;
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
|
复杂度分析:



